neurology brain and spine guide

Neurology explores the intricate brain-spine connection‚ vital for controlling bodily functions. The Brain & Spine Foundation offers guidance‚ while research highlights the impact of neurological impairments on self-concept.
1.1 Overview of Neurology as a Medical Field
Neurology is a medical specialty focusing on the diagnosis‚ treatment‚ and management of disorders affecting the nervous system. It encompasses the brain‚ spinal cord‚ and peripheral nerves‚ addressing conditions like headaches‚ myelopathy‚ and central sensitization. Neurologists use advanced techniques such as neuroimaging and clinical exams to assess neurological function. The field emphasizes understanding the brain-spine connection‚ crucial for motor and sensory functions. Organizations like the Brain & Spine Foundation provide essential resources for patients‚ highlighting the importance of multidisciplinary care. Neurology’s scope extends to chronic pain syndromes and degenerative conditions‚ ensuring comprehensive patient support and advancing therapeutic approaches.
1.2 The Brain-Spine Axis: Importance and Interconnectedness
The brain-spine axis is a critical network ensuring the seamless communication between the central nervous system and the body. This interconnectedness enables motor function‚ sensory perception‚ and reflex responses. Damage to the spinal cord or brain can disrupt this axis‚ leading to conditions like cervical spondylotic myelopathy or central sensitization. The spinal cord acts as a relay station‚ transmitting signals between the brain and peripheral nerves. Understanding this connection is vital for diagnosing and treating neurological disorders. Organizations like the Brain & Spine Foundation emphasize the importance of this relationship‚ providing resources to manage related conditions. This interconnected system underscores the complexity and fragility of neurologic function‚ requiring specialized care and support.
Common Neurological Conditions Affecting the Brain and Spine
Neurological conditions like central sensitization and cervical spondylotic myelopathy impact the brain and spine‚ causing chronic pain and spinal cord compression‚ affecting motor function and sensation.
2.1 Headaches: Causes‚ Diagnosis‚ and Management
Headaches are a common neurological symptom‚ often caused by tension‚ migraines‚ or underlying conditions. Diagnosis involves patient history‚ physical exams‚ and sometimes imaging. Management includes lifestyle changes‚ medications‚ and stress reduction. Referrals to specialists may occur due to persistent symptoms or red flags like sudden onset or neurological deficits. Patient pressure and GP characteristics influence referral decisions‚ as noted in studies. Proper diagnosis is crucial to rule out serious conditions‚ ensuring effective treatment plans are implemented. Early intervention can significantly improve quality of life for those affected by chronic or debilitating headaches.

2.2 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Degenerative Spinal Condition
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a degenerative condition caused by spinal cord compression in the cervical spine. It often affects older adults and can lead to numbness‚ weakness‚ and loss of coordination. Symptoms may progress slowly‚ and in severe cases‚ surgical intervention is necessary to relieve pressure and prevent further damage. Early diagnosis is critical‚ as delayed treatment can result in permanent neurological deficits. This condition highlights the importance of monitoring spinal health and seeking specialized care when symptoms arise. Proper management can significantly improve quality of life and functional outcomes for patients.
2.3 Central Sensitization: Understanding Chronic Pain Syndromes
Central sensitization is a complex condition characterized by increased sensitivity of the central nervous system‚ leading to chronic pain. It often arises after injuries or inflammation‚ causing heightened pain perception. Patients may experience widespread pain‚ hypersensitivity‚ and emotional distress. Diagnosis involves ruling out other conditions and assessing pain patterns. Management typically combines medications‚ physical therapy‚ and psychological support. This condition emphasizes the brain-spine connection‚ as central nervous system changes can amplify pain signals. Early intervention is crucial to improve quality of life and reduce long-term disability. Understanding central sensitization is key to addressing chronic pain syndromes effectively.
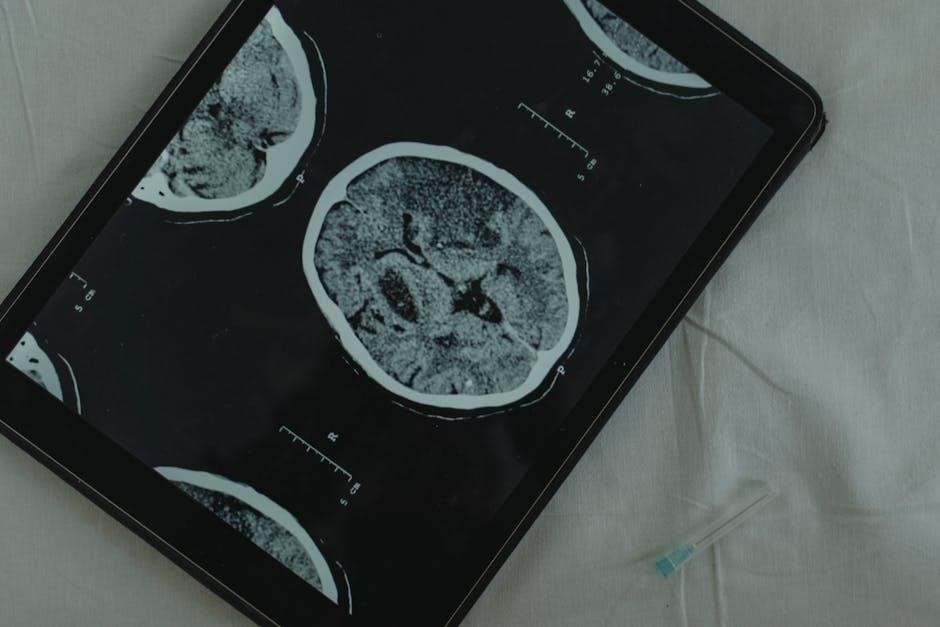
Diagnostic Techniques in Neurology
Neuroimaging and clinical exams are vital for diagnosing brain and spine disorders‚ providing insights into structural and functional abnormalities that guide effective treatment plans and patient care.
3.1 The Role of Neuroimaging in Diagnosing Brain and Spine Disorders
Neuroimaging plays a pivotal role in diagnosing brain and spine disorders by providing detailed visualizations of structural abnormalities. Techniques such as MRI and CT scans allow clinicians to identify conditions like cervical spondylotic myelopathy‚ central sensitization‚ and atlantoaxial instability. These imaging modalities are crucial for assessing the extent of spinal cord compression‚ inflammation‚ or damage to neurovascular structures. Early and accurate diagnosis through neuroimaging enables timely interventions‚ improving patient outcomes. The Brain & Spine Foundation emphasizes the importance of advanced imaging in guiding treatment plans‚ ensuring that patients receive appropriate care for their specific neurological conditions.
3.2 Clinical Examinations: Assessing Neurological Function
Clinical examinations are essential for evaluating neurological function‚ providing insights into brain and spine health. These assessments typically include a detailed patient history‚ physical examination‚ and neurological tests to evaluate motor strength‚ reflexes‚ and sensory function. Clinicians use these tools to identify signs of conditions like central sensitization‚ cervical spondylotic myelopathy‚ or atlantoaxial instability. Patient-reported symptoms‚ such as chronic pain or numbness‚ guide further investigations. The findings from clinical exams help differentiate between neurological and musculoskeletal issues‚ ensuring accurate diagnoses. This step is crucial before advanced imaging or referrals to specialists‚ as it lays the foundation for targeted treatment plans and improved patient outcomes.

Treatment Options for Brain and Spine Conditions
Treatments range from surgical interventions for conditions like cervical spondylotic myelopathy to non-surgical approaches‚ including medications and therapy. Advanced imaging often guides these personalized treatment plans.
4.1 Surgical Interventions: When and Why They Are Necessary
Surgical interventions are often essential for conditions like cervical spondylotic myelopathy‚ where chronic spinal cord compression requires decompression. Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases where non-surgical methods fail to alleviate symptoms or halt disease progression. Neurosurgeons play a critical role in managing these complex cases‚ utilizing advanced techniques to address issues like tumors‚ bleeding‚ or structural instability. The decision to operate is based on thorough diagnostic evaluations‚ including imaging and clinical assessments‚ ensuring that surgery is the most effective option for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
4.2 Non-Surgical Approaches: Medications‚ Therapy‚ and Lifestyle Changes
Non-surgical approaches are often the first line of treatment for many neurological and spinal conditions. Medications such as muscle relaxants‚ pain relievers‚ and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage symptoms like pain and inflammation. Physical therapy is another cornerstone‚ improving mobility and strength while reducing stiffness. Lifestyle changes‚ including adopting a balanced diet‚ regular exercise‚ and stress management‚ can significantly impact recovery and overall well-being. Cognitive-behavioral therapy may also be recommended to address chronic pain syndromes like central sensitization. These methods are tailored to individual needs and aim to enhance quality of life without the risks associated with surgical interventions.

Support and Resources for Patients
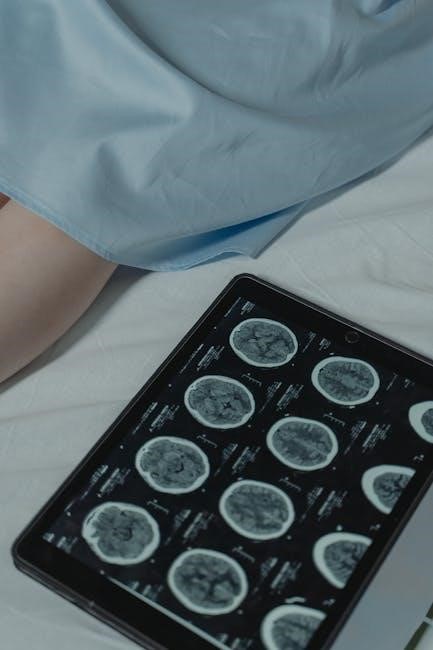
Organizations like the Brain & Spine Foundation provide vital support through educational materials and guides‚ helping patients understand and manage their conditions effectively.
5.1 The Role of Organizations Like the Brain & Spine Foundation
Organizations like the Brain & Spine Foundation play a crucial role in providing comprehensive support to patients and families affected by neurological conditions. They offer detailed guides‚ educational materials‚ and resources to help individuals understand their diagnoses and manage symptoms effectively.
These organizations also facilitate access to specialist care and rehabilitation services‚ ensuring patients receive the best possible support. By fostering a sense of community and providing emotional support‚ they empower patients to navigate their conditions with confidence and resilience.
5.2 Patient Guides and Educational Materials for Better Understanding
Patient guides and educational materials are essential tools for individuals navigating neurological and spinal conditions. These resources‚ often created by medical professionals‚ provide clear explanations of complex topics‚ helping patients and caregivers make informed decisions.
From detailed guides on conditions like Central Sensitization to practical advice on managing symptoms‚ these materials empower individuals to take an active role in their care. By fostering better understanding‚ they reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being‚ ensuring patients are equipped to manage their health effectively.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.